Solar Inverter Market Development Trends In Brazil
 Apr 10,2025
Apr 10,2025
 XINDUN
XINDUN
Brazil is a country with unstable power supply and serious power shortage. As of 2024, Brazil's power structure is still dominated by hydropower, but due to climate change and dry seasons, hydropower brings the risk of unstable supply, exacerbating energy shortages and rising electricity prices. This further increases the energy burden on households and businesses. In response to these challenges, the Brazilian government actively promotes the development of renewable energy - solar power and wind power. As the core equipment of solar systems, solar inverters play a vital role in this process, and market demand continues to rise. As one of the largest solar markets in Latin America, how did solar inverters achieve rapid development?

I.Brazil's power structure and current situation
1. Power structure
Brazil's power structure is dominated by hydropower, accounting for about 60%. The second largest energy source is solar power, with an installed capacity of over 55 GW, accounting for 22.2% of the country's power structure. More than 5,500 cities in Brazil have installed distributed solar systems, and all states have large centralized solar power stations. Among users of self-generated solar power, residential accounts for the highest proportion, reaching 69.2%, while commercial places and rural properties account for 18.4% and 9.9% respectively. From January to March 2025 alone, Brazil added more than 147,000 solar systems, providing electricity to 228,700 households. Since 2012, Brazil's solar industry has attracted more than 251.1 billion reais in investment, created more than 1.6 million green jobs, and contributed 78 billion reais in taxes to the Brazilian government. With the increasing global attention to renewable energy, Brazil's solar industry is becoming an important pillar of the country's energy transformation, and Brazil will also attract more attention in the global green energy market.
2. Power shortage
Brazil has long been dominated by hydropower, but hydropower is significantly affected by climate change, especially in the dry season, when reservoir water levels drop and power capacity is greatly weakened. According to data from the Brazilian National Electric System Operator (ONS), at the beginning of 2024, the water levels of major reservoirs in Brazil dropped by about 30% compared with the same period in previous years, resulting in a decrease in hydropower and a shortage of power supply in many regions. In recent years, due to frequent droughts caused by climate change, Brazil has faced a shortage of power supply many times, and has carried out large-scale power restrictions and power outages many times. It seriously affects the daily life of the Brazilian people and the normal operation of enterprises. In order to solve the problem of power supply, they have to turn to new energy power, and solar energy and wind power have received great attention in the market.
3. Rising electricity prices
Brazil's electricity prices continue to rise. According to data from the Brazilian National Electricity Agency (ANEEL), in the first quarter of 2024, Brazil's average electricity price rose by about 18% year-on-year, and the price increase in some areas even exceeded 25%. Tight power supply and aging infrastructure are the main reasons for the increase in electricity prices. High electricity prices have increased the energy burden on households and businesses, prompting more people to turn to solar power to reduce long term electricity bills.
As a key part of improving system efficiency and stability, the market demand for solar inverters has increased significantly. In the industrial and commercial fields, the demand for high efficiency inverters continues to rise.
4. Low grid coverage
Brazil has a vast territory and incomplete grid coverage. Many remote areas have long faced the problem of insufficient power supply. According to statistics from the Brazilian Energy Research Company (EPE), in 2024, about 15% of remote areas in Brazil will still not be connected to the national grid. The grid coverage rate in the Amazon region and some rural areas is low, and residents and small commercial users often cannot obtain a stable power supply. These areas usually rely on diesel generators for power supply, which is not only costly but also highly polluting. Solar power systems can provide clean and reliable power solutions for these areas. According to ABSOLAR data, in the first quarter of 2024, the installed capacity of off-grid solar systems in Brazil increased by about 40% year-on-year. The demand for off-grid inverters continues to grow. These devices can provide independent power solutions to meet the electricity needs of residents and small businesses in remote areas. Promote the development of the Brazilian solar market.
II.How is the electricity price in Brazil?
In 2015, the Brazilian National Electricity Agency (ANEEL) created a color-coded system for electricity price surcharges. The system uses different colors to intuitively reflect the variability of the cost of electricity energy, which in turn affects the electricity price for consumers. The green symbol represents that the cost of electricity is at a normal level, and consumers do not need to pay additional electricity surcharges; the yellow symbol means that the cost of electricity has increased, and consumers need to pay an additional 29.89 reais for every megawatt (MWh) of electricity consumed; the red level 1 indicates that the cost of electricity has increased further, and an additional 65 reais is required for every 1 MW of electricity consumed; the red level 2 represents the highest level of electricity costs, and an additional 97.95 reais is required for every 1 MW of electricity consumed. In October 2024, due to the severe drought that caused insufficient power from hydropower stations, Brazil's electricity price mark was set as "Red Level 2", that is, for every 100 kWh (100 kWh) of electricity consumed, consumers will be charged an additional fee of 7.877 reais on their electricity bills. This has greatly increased the electricity costs of households and businesses, bringing a heavy economic burden to electricity consumers.
In November 2024, as Brazil gradually increased its use of solar power and improved power conditions, the country reduced its electricity fee standards from the original red mark to the yellow electricity price charge mark from November 1. Under the yellow mark, the electricity fee surcharge for every 100 kWh (kWh) of electricity consumed is 1.885 reais, which is significantly lower than the red level 2 fee, which directly reduces the pressure on consumers' electricity costs. The decline in electricity costs is due to solar power, prompting more and more households and businesses to choose solar power.
III.Challenges facing the Brazil solar energy market
In recent years, Brazil's solar industry has continued to develop. According to statistics from the Brazilian energy department, the country's solar installed capacity has been rising year by year, but it is still far from meeting the needs of the domestic market. Below we will analyze the challenges facing the solar energy market:
1.Import tariffs and local production barriers
Import tariffs impact cost structure: In 2024, Brazil will significantly increase the import tax rate of solar modules from 10.8% to 25%. This move directly affects the import cost of inverters. Inverter production is highly dependent on imported parts, and the increase in tariffs has significantly increased product costs. For example, some international brands of inverters, their key electronic components are mostly imported from abroad. After the tariff increase, the cost pressure is directly transferred to the price of end products. For buyers and consumers in the Brazilian market, the price increase has reduced the cost performance of products and suppressed market demand. International brand products that originally had price advantages have weakened their advantages in market competition due to tariff factors. Some small companies are even facing operating difficulties and are unable to withstand the pressure brought by rising costs. They have to reduce their business scale or exit the market. International cooperation should be actively promoted. International brands can consider establishing production bases in Brazil, making use of local resources and labor, reducing the impact of import tariffs, achieving localized production, and reducing dependence on imported parts.
Local production barriers: Although the Brazilian government has vigorously promoted the localization of inverter production to reduce dependence on imported products and enhance the competitiveness of local industries, local companies face many challenges in terms of technology and scale. In terms of technology, there is a gap with the international advanced level, and it is difficult to produce inverter products with the same performance and quality. With long-term R&D investment and technological accumulation, international brands are leading in key technical indicators such as inverter conversion efficiency and intelligence. Due to the lack of core technology, local companies lack competitiveness in the market. In terms of scale, local production has not yet formed a scale effect, and production costs remain high. Due to limited output, it is impossible to reduce unit costs through large-scale production, and it is at a disadvantage in price competition with international brands. The imperfect local supply chain and unstable supply of parts have also restricted the development of local production companies, making it difficult for them to compete with international brands in market competition. The supply chain should be optimized to improve the cost performance of inverters to make up for the cost increase caused by import taxes.
2. Inverter brand competition
International brands and market competition: In the Brazilian solar energy market, international brands, especially Chinese brands, have shown strong competitiveness. Companies like Huawei and Xindun Power, through localized layout, have not only brought advanced technology, but also provided a diversified product line to meet the needs of different application scenarios. These companies continue to invest in research and development and continuously launch high-performance and high efficiency inverter products. For example, the new inverters they developed have significantly improved conversion efficiency, reduced energy loss, and brought higher economic benefits to users. At the same time, international brands have improved market response speed and customer satisfaction by establishing local sales teams and after-sales service networks. In contrast, Brazilian local brands have obvious gaps in technology research and development and product diversification, making it difficult to compete with international brands in the high-end market, and their market share is constantly affected by international brands. We should strengthen cooperation with international brands, enhance brand promotion, and enhance customer trust.
Difficulty in survival for local brands: Brazilian local brands are mainly concentrated in the mid and low end markets, trying to attract cost sensitive customers through price advantages. As international brands continue to optimize their cost structure and launch more cost effective products, the price advantage of local brands is gradually disappearing. Local brands have insufficient investment in technology research and development, and their product upgrades are slow, making it difficult to meet the market's demand for high performance, intelligent inverters. In terms of after-sales service, local brands are also relatively weak and cannot provide service quality comparable to that of international brands. With their brand influence and market reputation, international brands have gained more project orders and customer trust in the Brazilian market, further squeezing the living space of local brands. Many local brands are facing severe survival challenges. Market positioning should be clarified, product quality should be improved, and inverters suitable for Brazil's power needs should be produced.
3. Inverter technical requirements
Strict standards and technical difficulties of on grid inverters: In Brazilian cities and industrial areas, on grid inverters are in high demand, but face strict technical requirements. On grid inverters need to have efficient DC to AC conversion capabilities to ensure that the electricity generated by solar power systems can be efficiently integrated into the local power grid. At the same time, strict grid access standards must be met, including grid fault protection, power regulation, power quality monitoring and other functions to ensure the stable operation of the power grid. However, the grid infrastructure in some parts of Brazil is aging and the grid stability is poor, which puts higher requirements on the technical performance of on grid inverters. When some old grids are connected to a large amount of solar power, voltage fluctuations and harmonics are prone to occur, requiring on grid inverters to have stronger adaptability and adjustment capabilities. With the development of intelligent grids, on grid inverters must also have the ability to communicate and work with smart grids, which is a technical problem for many companies and requires a lot of R&D resources to solve. We should improve our technological innovation capabilities and produce inverters that meet Brazilian grid standards.
Challenges of environmental adaptability and reliability of off-grid inverters: Remote areas, farms and small businesses in Brazil have a large demand for off grid inverters. Off grid inverters must not only convert the direct current(DC) generated by solar panels into alternating current(AC), but also have the ability to operate independently and be used in conjunction with energy storage devices (such as batteries) to provide stable power for local power equipment. However, the environmental conditions in these areas are harsh, such as high temperature, high humidity, strong electromagnetic interference, etc., which put extremely high requirements on the reliability and environmental adaptability of off grid inverters. Some off-grid inverters are prone to failure in harsh environments, affecting the stability of power supply. Off-grid inverters also need to have good anti-interference capabilities to cope with the complex electromagnetic environment in remote areas. In terms of technology research and development, how to improve the reliability and stability of off grid inverters in harsh environments and reduce the failure rate is a major challenge facing companies. The inverter should adopt high heat resistance and moisture-proof design to improve the stability of the inverter in high temperature and high humidity environments.
Complex energy management challenges of hybrid inverters: As the trend of combining solar energy with energy storage gradually becomes popular in Brazil, the demand for hybrid inverters continues to increase. Hybrid inverters need to have complex energy management functions that can accurately control the flow and conversion of electric energy and realize intelligent switching between solar power, grid power supply and energy storage. There are many technical challenges in achieving efficient energy management. Switching between different energy sources requires precise control algorithms and sensor monitoring to ensure that the switching process is smooth and does not affect the stability of power supply. At the same time, hybrid inverters also need to automatically adjust power consumption strategies based on factors such as peak and valley changes in electricity prices and load demand, which places high demands on their intelligence and computing power. At present, some hybrid inverters on the market have defects in energy management, resulting in low energy utilization efficiency and poor user experience. Enterprises need to further strengthen technology research and development to improve the energy management level of hybrid inverters.
4.Insufficient local installation and maintenance services
Shortage of professional technicians: A key problem with local installation and maintenance services in Brazil is the shortage of professional technicians. Many installers lack in-depth understanding and installation experience of solar inverter systems, resulting in uneven installation quality. The installation of solar inverter systems requires professional knowledge and skills, including electrical knowledge, system debugging, etc. Due to the lack of professional training, some installers may encounter problems such as wiring errors and improper parameter settings during the installation process, which not only affects the performance and service life of the inverter, but also may cause safety hazards. For example, incorrect wiring may cause the inverter to short-circuit, causing serious accidents such as fire. When the inverter fails, due to the lack of professional knowledge of the technicians, it is difficult to diagnose and solve the problem quickly and accurately, which prolongs the equipment downtime and causes economic losses to users. Xindun can help installation engineers complete the installation under the correct guidance by providing installation instructions and video guidance. Provide installation and maintenance training for dealers and technicians.
Imperfect after-sales service network: Brazil's after-sales service network is insufficient in terms of coverage and service quality, especially in remote areas, where inverters often cannot be repaired in time after failure. Many areas lack professional after-sales service centers, and users find it difficult to find reliable repair channels when they encounter problems. Even in some areas where there are after-sales service centers, due to the limited number of service personnel, they cannot respond to all users' maintenance needs in time. The imperfection of the after-sales service network is also reflected in the untimely supply of parts. When the inverter needs to replace parts, the maintenance cycle may be extended due to supply chain problems. This makes users worry about the reliability of solar inverter systems, which to a certain extent hinders the further development of the market. In order to solve these problems, it is necessary to increase the training of local technicians and improve their professional skills. At the same time, companies should strengthen the construction of after-sales service networks, set up service centers in more areas, improve service response speed, and improve the parts supply system. Investment in the construction of after-sales service networks in Brazil should be increased, service centers should be set up in more areas, service outlets should be reasonably arranged, and service response speed should be improved. Through remote monitoring technology, the remote fault diagnosis capability of inverters can be improved to reduce maintenance costs. Xindun's solar power system is equipped with RS485 remote monitoring function, which can help users monitor the inverter status in real time.
IV. Development prospects of solar power in Brazil
1. Rich solar energy resources
Most of Brazil is located in the tropics, with long and strong sunshine hours. The average annual sunshine hours in Brazil are 2,200-2,800 hours, and the northeastern region (such as Ceará State) exceeds 3,000 hours. In the dry season (May-October), the average daily peak sunshine hours can reach 6-7 hours. This has laid a solid foundation for solar power. Brazil also has large tracts of land required for the installation of solar power equipment, and has silicon mines required for the production of solar power equipment, providing good energy for the development of the solar power industry.
2. National policy support
The Brazilian government actively promotes energy transformation and aims to achieve a 45% share of renewable energy by 2030. The Brazilian government encourages the development of solar power and energy storage projects by regularly holding renewable energy auctions. The auction mechanism provides investors with long term power purchase agreements (PPAs) to ensure the economic feasibility of the project. The government also set clear solar power targets and allocated capacity through auctions to promote the large-scale application of solar and energy storage technologies. This policy has attracted a large number of domestic and foreign companies to participate, accelerating the growth of Brazil's solar market. In order to reduce the investment cost of solar and energy storage projects, the Brazilian government has introduced tax exemptions and subsidy policies. From January 2024, Brazil will impose an import tariff of 10.8% on solar modules, and further increase it to 25% in July 2025. Sao Paulo State, Minas Gerais State and other states have extended the state tax exemption for solar equipment imports until the end of 2026, and the equipment cost can be reduced by 12%-18%. Sao Paulo State has set up a special fund of 500 million reais to provide installation subsidies of up to 30% for rooftop solar projects. Piauí State promotes "solar + energy storage" microgrids in remote areas, and the state government bears 30% of the project costs. Brazil's "Basic Energy Income Plan" launched in 2025 provides a 50% electricity bill discount to low income households, covering about 20 million households, directly stimulating distributed solar demand. For example, households in the northeastern state of Ceará can reduce electricity bills by 40%-60% after installing solar.
The government also provides a net metering policy for distributed solar power, allowing users to sell excess electricity back to the grid, further incentivizing households and small businesses to install solar systems. To support the widespread application of solar and energy storage technologies, the Brazilian government has launched a grid infrastructure upgrade program. The program aims to improve grid access capabilities in remote areas and enhance the efficiency of power transmission across the country. The government also encourages the private sector to participate in grid construction and accelerate project implementation through the public private partnership model (PPP). Under the active promotion of national policies, the development of the solar energy market has been accelerated.
3. Market demand growth
With the development of Brazil's economy and the advancement of urbanization, electricity demand continues to grow. According to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), in 2022, Brazil's installed solar power capacity ranked 8th in the world (more than 24 gigawatts at the time). Between January and September 2023, solar installed capacity increased by 3 gigawatts. According to the Brazilian Photovoltaic Solar Energy Association (ABSOLAR), as of February 2024, Brazil's total installed solar power capacity is estimated to be approximately 38.4 gigawatts, accounting for approximately 17.0% of the country's power matrix. The Brazilian Solar Energy Association predicts that by 2025, new investments in the solar industry will exceed 39.4 billion reais, new installed capacity will exceed 13.2 GW, and cumulative installed capacity will reach 64.7 GW. Wind and solar energy are expected to become the country's main sources of power, and may reach 47% of total installed capacity by 2040. This means that there will be a potential market worth up to $11 billion by 2040. It is predicted that the scale of Brazil's solar energy market will continue to expand in the next few years, and the installed capacity of solar energy will continue to grow, and it is expected to become one of the largest solar energy markets in Latin America.
Brazil's industrial and commercial demand for solar energy is also growing. Due to the large amount of electricity consumption and high prices in industrial and commercial industries, enterprises can significantly reduce operating costs and improve market competitiveness by adopting solar power generation. Especially in high energy consuming industries such as agriculture, manufacturing, and commercial centers, solar systems have become an important means for enterprises to reduce energy consumption and improve economic benefits. More and more companies are beginning to pay attention to carbon emissions and sustainable development. The use of solar energy can not only save costs, but also enhance brand image and meet international environmental standards.
4. Technological progress and cost reduction
With the development of the global solar industry, the improvement of China's solar industry manufacturing capacity, the continuous progress of solar power technology, the continuous improvement of the efficiency of solar modules, inverters and energy storage batteries, and the continuous decline in power costs have greatly improved the economic efficiency of solar power. In recent years, the conversion efficiency of solar modules has increased from about 15% in the past to more than 20%, and the intelligent and multifunctional design of inverters has also improved the energy efficiency and stability of the overall system. The popularization of large-scale production and automated manufacturing, as well as the maturity of the global solar supply chain, have greatly reduced the levelized cost of electricity (LCOE) of solar power. According to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), the cost of solar power in Brazil has dropped to less than US$0.03 per kilowatt-hour in 2024, making it one of the most economical energy sources.
5. International cooperation and win-win development
Brazil actively seeks cooperation with foreign countries in the field of solar power under the framework of international cooperation such as the joint construction of the "Belt and Road". By introducing advanced technology, capital and experience, Brazil has been able to accelerate the development of the solar power industry. At the same time, Brazil is also committed to exporting its successful experience and technological achievements to other countries to achieve win-win development. This international cooperation model will not only help the rapid development of Brazil's solar power industry, but also promote the common progress of the global renewable energy industry.
V.What kind of inverter suitable for Brazil?
In Brazil, power supply issues and high electricity prices have driven the development of the solar energy market. As a component of the solar power system, solar inverters directly affect the efficiency of power and the way electricity is used. According to the power demand and application scenarios in different regions of Brazil, which type of off grid inverter, on grid inverter and hybrid inverter is more suitable?
1.On grid inverter
The on grid inverter is a key device that converts the direct current (DC) generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) and injects it directly into the grid. It ensures that the output power is synchronized with the grid by monitoring the voltage and frequency of the grid in real time. Brazil's net metering policy allows users to inject excess power into the grid and obtain electricity bill deductions, which greatly increases the enthusiasm of households and businesses to install solar energy systems. It is suitable for areas with relatively complete Brazilian power grids. For large industrial and commercial users, the on grid system can not only save electricity bills, but also improve energy independence.
2. Off grid inverter
Off grid inverters are suitable for independently operated solar energy systems, usually used in conjunction with energy storage batteries. It converts the direct current(DC) generated by solar panels into alternating current(AC) for load use, and stores excess power in batteries for use at night or on cloudy days. It is suitable for some remote rural areas, mountainous areas or islands in Brazil where the power grid is not covered. The off grid system enables these areas to achieve energy self sufficiency. At the same time, the government is also vigorously promoting the application of renewable energy in remote areas, further promoting the market growth of off grid inverters.
3. Hybrid inverters
The hybrid inverter combines on grid and off grid functions, and can connect to the grid, solar panels and energy storage systems at the same time. It intelligently switches working modes according to power demand and grid status, giving priority to solar power, and storing or injecting excess power into the grid. It is suitable for users who want to connect to the grid to save electricity bills and need energy storage to cope with grid instability. In some parts of Brazil, such as the northeast and some industrial areas, the power supply is not stable, and frequent power outages affect production and life. The hybrid inverter can automatically switch to the energy storage system for power supply to ensure the continuity of power supply. In hospitals, schools, shopping malls and other scenarios, the continuity of power supply is required to be high. Once a power outage occurs, it will cause serious losses. Hybrid inverters can not only cope with rising electricity prices, but also provide stable power support and can respond to different product demands in the market.
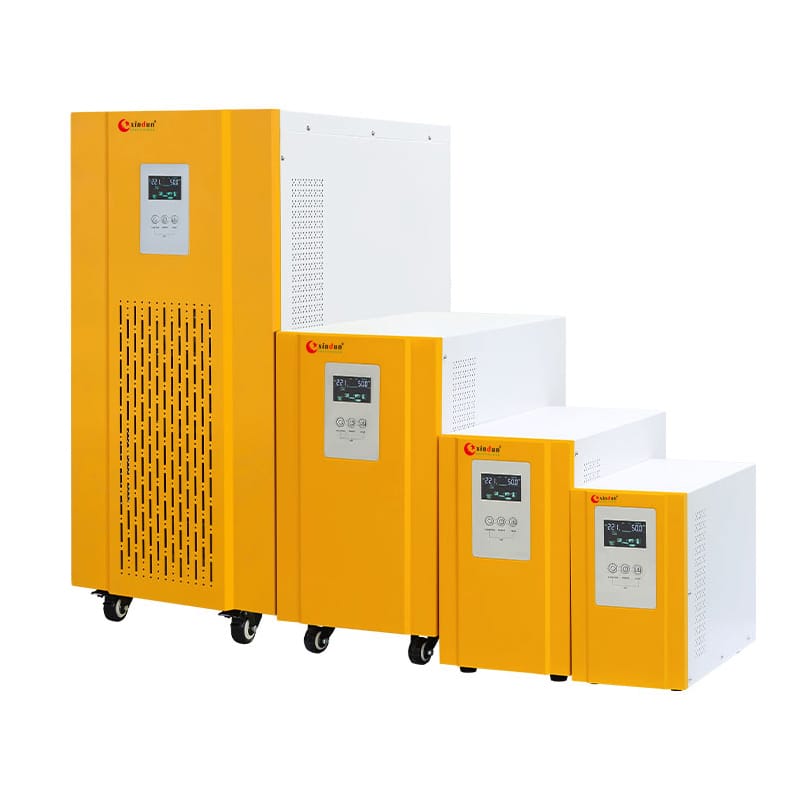
VI. Recommended solar inverters for Brazil
With the rapid development of the Brazil solar market, solar inverters are an important part of the solar power system. It is crucial to choose inverters that are suitable for Brazil's power needs. Whether it is household user, industrial and commercial project, or an off grid system in remote area, it is necessary to choose the appropriate inverter type according to specific needs. Xindun will recommend 4 solar inverters suitable for the Brazil market:
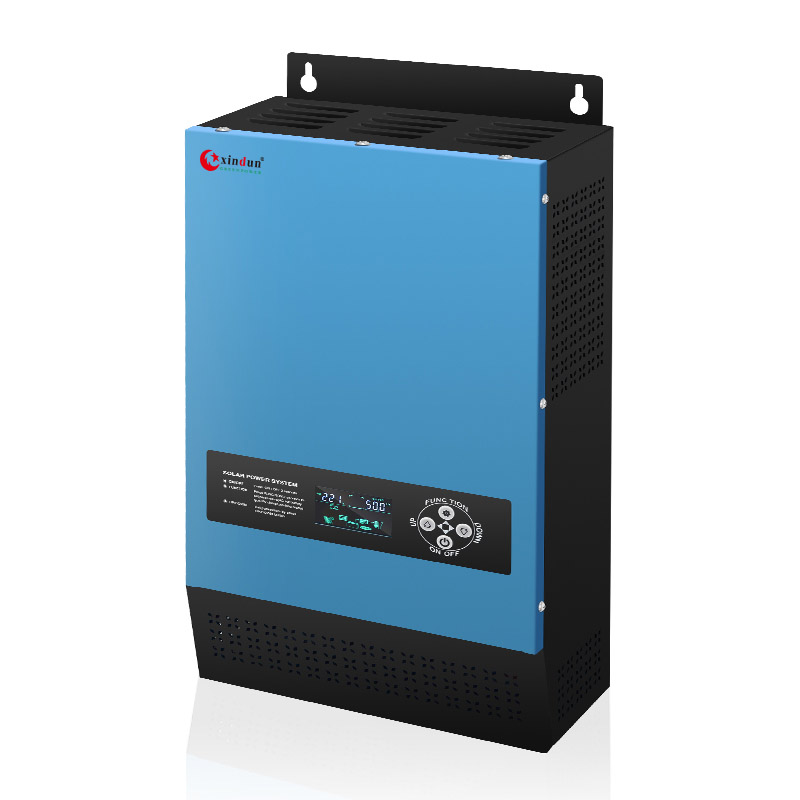
Xindun LS Solar Inverter
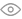
Xindun LS solar inverter 1KW-6KW, providing DC 12V/24V/48V to AC 110V/120V/220V/230V/240V
LS series inverter is an efficient and stable split phase solar inverter, suitable for the Brazilian market with unstable power supply and high demand for backup power. Adopting toroidal low loss transformer design, the inverter efficiency is as high as 98%, and the pure sine wave output ensures stable power quality. Built-in MPPT controller (optional) maximizes solar power efficiency and supports adjustable mains charging current of 0~30A, which can flexibly deal with the problem of unstable power supply in Brazil. The inverter supports diesel (gasoline) generators and can work reliably in remote areas or when the mains power is unstable. At the same time, the LS series has a starting capacity of up to 3 times the peak power, which can drive equipment with large instantaneous power demand, such as air conditioners, water pumps, etc., which is very suitable for Brazilian families, agriculture and small commercial users. It supports split-phase voltage output of 110V/220V or 120V/240V, and can flexibly adapt to the power grid standards of different regions to meet Brazil's diverse power needs.
Xindun WD Solar Inverter

Xindun WD solar inverter 500W-40kW, providing DC 12V/24V/48V/96V/192V/240V/384V to AC 110V/120V/220V/230V/240
WD series inverter is an efficient and reliable low frequency pure sine wave inverter, suitable for the Brazil market with high electricity prices and frequent power supply fluctuations. Its mains charging current is adjustable from 0 to 20A, allowing users to flexibly configure the energy storage system according to different battery capacity requirements to improve energy utilization. The inverter has adjustable working modes of mains priority, inverter priority, and energy-saving mode. Users can switch freely according to the grid conditions and power demand to achieve optimal energy management. In areas of Brazil where power outages are common, inverter priority can be switched instantly to ensure the operation of key equipment. When the mains power is stable and the electricity price is low, the mains priority can reduce costs; the energy saving mode is suitable for low power scenarios. At the same time, it is compatible with diesel (gasoline) generators, ensuring continuous power supply even in remote areas or when the mains power supply is unstable. For the Brazilian market, this inverter not only provides stable power output, but also can adapt to different power environments, allowing households, shops and small industrial users to effectively reduce electricity costs when electricity prices rise.
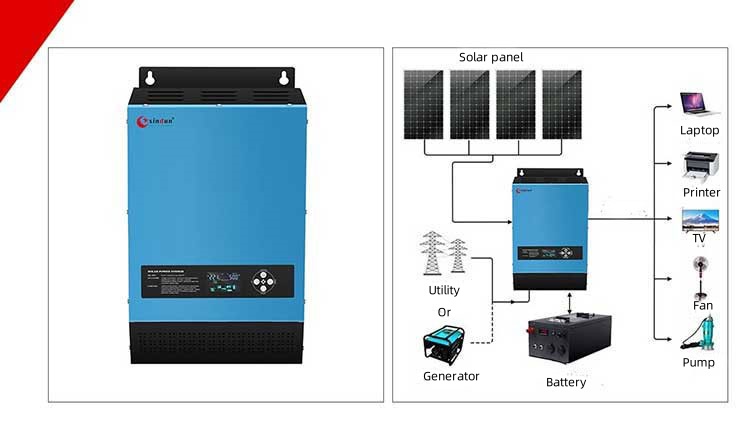
Xindun HFP On Grid And Off Grid Hybrid Solar Inverter
Xindun HFP on-grid and off-grid hybrid solar inverter 1.3KW-12.3KW, providing DC 12V/24V/48V to AC 220V/230V/240V
The HFP series is a high-frequency designed on grid and off grid hybrid solar inverter with high power density, small size, and high overall efficiency, suitable for a variety of application scenarios in homes, industry and commerce, and remote areas. The bidirectional energy storage design not only allows solar and mains power to charge the battery at the same time, but also supports battery-free operation mode, allowing users to flexibly respond to different power needs. Built in MPPT solar controller to maximize the use of solar energy. It has adjustable on-grid, off-grid, and hybrid modes. Users can freely choose the optimal mode according to the local power grid conditions, flexibly respond to the problem of unstable power supply, and is suitable for areas where the Brazilian power grid fluctuates frequently. The HFP inverter supports the function of feeding to the grid, and users can sell excess power back to the grid, making full use of Brazil's net metering policy and reducing electricity bills.
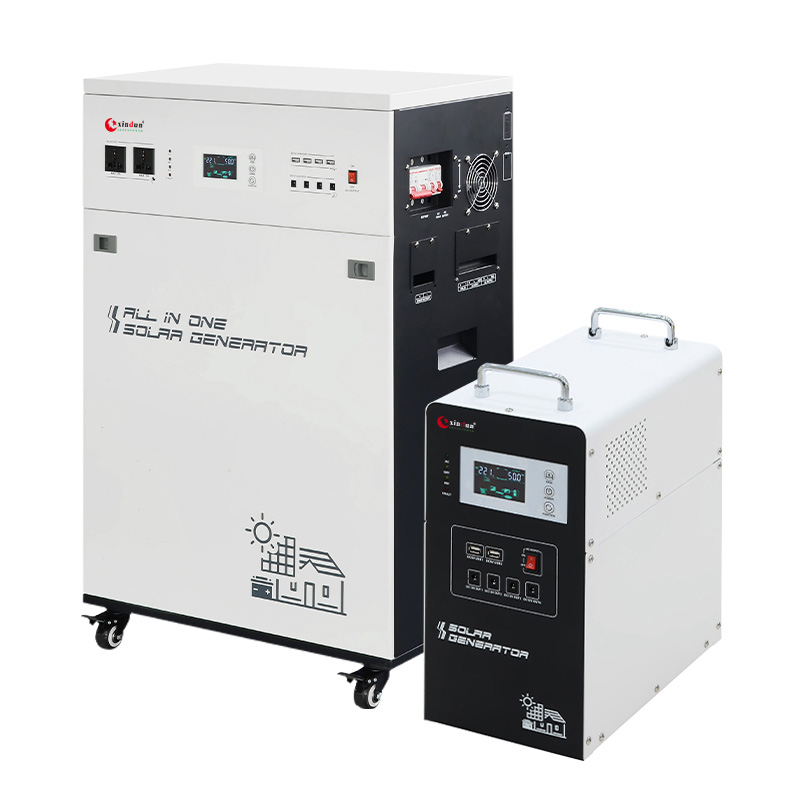
Xindun ESS-Li All In One Solar Power Generator

Xindun ESS-Li all in one solar power generator 300W-7000W, providing DC 12.8V/25.6V/51.2V to AC 110/120/220/230/240V
ESS-Li all in one solar power generator is an intelligent energy storage solution integrating solar controller, inverter and lithium battery. Its integrated design not only greatly simplifies the installation process, but also has a variety of convenient USB, DC ports and AC sockets to meet the diverse power needs of home and small commercial users. Supporting three charging methods of solar energy, city electricity and diesel generator, it is suitable for areas with unstable power supply in Brazil, ensuring that users can obtain stable power supply in different environments. It has comprehensive protection functions such as overvoltage, overtemperature, overload and battery BMS report to ensure safe and reliable operation of the system. Brazil has a hot climate and large load fluctuations in the power system. These protection functions effectively prevent equipment from being damaged due to abnormal conditions, extend the service life of the equipment, and provide users with safe and stable power guarantees. The inverter is also equipped with WiFi or APP remote monitoring function, which allows users to view the system operation status in real time and achieve efficient and autonomous energy management in the Brazil market with high electricity costs.
VII. Why choose Xindun as supplier?
In Brazil, the demand for electricity continues to rise, and the demand for efficient, stable and adaptable power products to the country's complex environment is becoming stronger. Xindun Power has been deeply involved in the inverter field for 20 years, focusing on the research and development, production and sales of solar power system products. We have brought together a professional team with rich experience in technology research and development, production management and quality control to provide customers with high-quality products. The products we produce include off-grid solar inverters, batteries, solar controllers and solar power systems. All products have passed the ISO9001 international quality management system certification and obtained a number of authoritative professional testing and certifications such as CE, IEC, CCC, etc., meeting the high standards of the Brazilian market. Whether it is daily household electricity use, commercial operations, or industrial manufacturing, our products can provide stable and reliable power support.
The Brazilian power market faces challenges such as rising electricity prices and unstable power grids, making efficient, stable and reliable solar inverters a rigid demand. Xindun has a modern production plant of more than 10,000 square meters and a professional R&D team of more than 30 people. We have strong production capacity and can provide customers with OEM/ODM customized services to meet the special needs of different customers. Brazil has a vast territory, and the climate, electricity habits and architectural characteristics of different regions vary significantly. Xindun Power can provide customized solar energy solutions based on these special environments. At the same time, Xindun Power provides comprehensive pre-sales and after-sales guarantee services. In terms of warranty, the low frequency inverter and solar controller have a 3-year warranty period, the high-frequency inverter has a 1-year warranty period, and customers can enjoy lifetime technical support.
Xindun Power's products have been sold well in more than 100 countries and regions around the world, and have established long-term cooperative relationships in Latin America, Southeast Asia, the Middle East, Africa and other markets. It can quickly respond to the needs of the Brazil market and provide customers with timely and professional technical support and services.
Against the backdrop of close economic and trade cooperation between China and Brazil, Brazil's demand for high quality solar products has exploded. As an industry leader, Xindun Power not only benefits from relevant policies and financial support, but also becomes a trustworthy power manufacturer in the Brazil market with our excellent product advantages and outstanding brand strength. If you are interested in Xindun Power's solar power system or inverter and other products, please fill in your information and needs in the window of our official website (https://www.xinduninverter.com), and Xindun's professional team will contact you quickly during working hours to help your business grow.


 Solar Inverter
Solar Inverter





 Hybrid Inverter
Hybrid Inverter





 Power Inverter
Power Inverter





 Split Phase Inverter
Split Phase Inverter

 Energy Storage Inverter
Energy Storage Inverter




 3 Phase Inverter
3 Phase Inverter




 Solar System Kits
Solar System Kits





 Solar Charge Controller
Solar Charge Controller


 Solar Battery
Solar Battery



 Asia
Asia
 Africa
Africa



 South America
South America
 Europe
Europe

 North America
North America

 Oceania & Antarctica
Oceania & Antarctica









 Home
Home Solar Power Inverters Recommendations For Ukraine Market
Solar Power Inverters Recommendations For Ukraine Market  Top Selling Products
Top Selling Products














