Solar Power Inverter Development in Indonesia
 Apr 26,2025
Apr 26,2025
 XINDUN
XINDUN
In the context of the global transition to green energy, Indonesia has become a highly anticipated emerging solar market in Southeast Asia. As the world's fourth most populous country and an archipelago, Indonesia has a severe power shortage and huge power demand due to its vast territory, numerous islands and unbalanced economic development. The government has begun to attach great importance to solar power, which has become a key strategy for future development.

With the advancement of solar technology and the reduction of costs, Indonesia has promoted the development of various solar projects, including large-scale ground power stations, industrial and commercial rooftop solar and off-grid systems, to promote the increase of solar installed capacity. As the "heart" of the solar power system, the solar inverter market has also ushered in explosive growth and has become a "new blue ocean" for many companies to compete. This article will take you to an in-depth understanding of the Indonesia solar inverter market and decode industry trends and opportunities.
I. Indonesia's power structure
As of August 2024, coal-fired power accounts for about 67%, natural gas for about 17%, hydropower for about 7.9%, geothermal for about 5.6%, and biomass and other renewable energy sources for only about 1.3%. Renewable energy accounts for only 12%-14% of Indonesia's power structure, but the installed capacity of solar accounts for only 0.1% of the total installed capacity, which is the lowest among G20 countries. Indonesia faces increasing pressure for energy transformation.
Therefore, the Indonesia government has set a goal to achieve a 23% renewable energy target by 2025, and plans to increase the proportion of renewable energy in the power structure to 44% by 2030. At the same time, this year Indonesia's sovereign wealth fund will invest about US$1 billion in all industries, with solar energy as one of the preferred priorities. However, achieving this goal faces challenges, including limitations of existing power infrastructure and high dependence on coal. In order to get rid of dependence on traditional energy generation and a single power structure, it is necessary to actively promote solar power.
II. What is the current situation of electricity in Indonesia?
Indonesia consists of more than 17,000 islands with a dispersed geographical structure, and the national main power grid cannot efficiently cover all areas. Although Indonesia, as one of the largest economies in Southeast Asia, has continued to grow in total power, there are still structural deficiencies in power supply. According to the 2024 data released by the Indonesian National Electricity Company (PLN), 27 million people across the country still cannot access the power grid stably, especially in the eastern regions such as Maluku, Sulawesi, Papua, Nusa Tenggara and other islands. Power outages, low voltage, and insufficient power coverage are very common, seriously affecting people's livelihood and industrial activities.
According to the "Indonesia Power Development Plan 2024 (RUPTL)", although the national power penetration rate in Indonesia has reached 99%, "having electricity" does not mean "having stable electricity". In rural areas, remote islands and other places, a large number of residents rely on diesel generators, which have high operating costs and serious environmental pollution, making reliable and clean solar energy a top priority.
At the same time, the distribution of Indonesia's national power grid is uneven. Java Bali concentrates nearly 60% of the country's population and industrial electricity, and the power supply is relatively sufficient or even in excess; while Sumatra, Kalimantan, and the eastern region are generally short of power supply, which restricts local economic development. Taking the eastern region as an example, the electrification rate of Papua Province is only 35.2%, and West Papua is even lower at 28%, which is the most backward region in the country. About 2,940 villages rely on small solar power, and 4,404 villages use independent diesel power stations. The electrification rate of Maluku Province is less than 40%, and North Maluku Province relies on diesel power, with a cost of up to US$0.3-0.5/kWh, and the power supply is intermittent. Due to the aging of the power grid, the region suffered a total of 12 large-scale power outages in 2024 alone, and the power supply stability was extremely poor. Data from 2024 shows that Indonesia's national average daily electricity consumption reached 43 GWh, with an annual growth rate of more than 4.7%, showing huge potential for growth in electricity demand.
Indonesia's power grid is dispersed, has weak connectivity, and has low coverage, resulting in insufficient cross-regional coordination capabilities and difficulty in forming an efficient and unified national power grid system. This geographical structure and infrastructure status make it difficult for centralized traditional power systems to cover the entire country, greatly limiting the radiation capacity of traditional energy.
To obtain a stable power supply, off-grid systems or hybrid solar power systems can be built in areas where the power grid is difficult to reach or the cost is too high. This can not only alleviate Indonesia's power shortage problem, but also provide many households that are not covered by the power grid with basic living electricity such as lighting, televisions, fans, and refrigerators, greatly improving the quality of life and safety, reducing the inconvenience and economic losses caused by power shortages, promoting the country's sustainable development strategy, and improving the country's economic level.
III.Is Indonesia's electricity price stable?
Indonesia's electricity price level has been under government regulation for a long time, but in fact there are many problems such as large regional differences, heavy subsidy pressure, and high electricity costs, and the electricity price situation is complicated. In the first two months of 2025, the Indonesian government implemented a policy of halving the electricity charges for households with a power of 2,200 VA or less. The electricity charges paid by these households in these two months were halved compared to the normal charging standards, and the economic burden on electricity consumption was reduced. Currently, households with a power of 2,200 VA or less in Indonesia no longer enjoy the halving preferential policy and are charged according to the normal electricity price standards. Even so, Indonesia's residential electricity prices are still at an upper-middle level in Southeast Asia. In Java and Bali, where the economy is relatively developed and the grid coverage is well-developed, the residential electricity price is relatively stable, with an average of about 2500-3000 rupiah per kilowatt-hour (about US$0.148-0.178). In some remote islands, such as the Maluku Islands and parts of Papua, the cost of electricity for residents has soared, as electricity supply relies on small diesel generators or unstable power grids, reaching 5,000-8,000 rupiah per kWh (about US$0.297-0.474), which is 2-3 times that of developed areas. The electricity price is expensive.
The commercial electricity price varies greatly depending on the size of the enterprise, the type of industry and the region. In the commercial areas of large cities such as Jakarta and Surabaya, the commercial electricity price is generally 3,500-4,500 rupiah per kWh (about US$0.208-0.267). For some high-energy-consuming commercial activities, such as large shopping malls and hotels, the electricity price may also increase by 10%-20%. In small commercial places in remote areas, due to poor power supply stability and high transmission costs, the commercial electricity price exceeds 6,000 rupiah/kWh (about US$0.355). High commercial electricity prices increase the operating costs of enterprises and inhibit the activity of commercial activities in remote areas.
The electricity price structure for industrial electricity is more complicated. Large industrial enterprises that sign long-term power purchase agreements with the Indonesian National Electricity Company (PLN) and have huge electricity consumption can enjoy relatively favorable electricity prices, usually between 2,800 and 3,800 rupiah per kilowatt-hour (about US$0.165-0.226). However, for many small and medium-sized industrial enterprises, especially those located in areas with weak power infrastructure, the cost of electricity remains high. Some manufacturing enterprises located in the eastern islands have industrial electricity prices exceeding 5,000 rupiah per kilowatt-hour (about US$0.297). This difference in electricity prices has led to uneven industrial development in different regions, and industrial enterprises in the eastern region are at a disadvantage in cost competition, which has restricted industrial transfer and coordinated development of regional economy.
The Indonesian government has long maintained stable electricity prices through fiscal subsidies. It is expected that electricity subsidies will reach 83 trillion rupiah (about US$5.11 billion) in 2025. Although the subsidy policy has alleviated the pressure of electricity costs for the public and enterprises to a certain extent, it has also brought a heavy burden to the fiscal budget. As Indonesia's economy develops and electricity demand continues to rise, if the energy structure is not changed and the proportion of solar power is increased to reduce power costs, the stability of electricity prices in the future will face greater challenges. For the majority of enterprises and residents, seeking renewable energy such as solar energy to generate electricity is expected to become an effective way to reduce electricity costs and ease power shortages, highlighting the importance and urgency of solar inverters in the Indonesia solar energy market.
IV. Development potential of solar power in Indonesia
1. Rich natural resources
Indonesia has abundant sunshine throughout the year, with an average annual sunshine duration of more than 2,600 hours and an average sunshine duration of more than 4.8 hours per day, which lays the foundation for solar power. The potential installed capacity of solar energy is as high as 207.8GW, but as of the end of 2024, the actual development volume only accounts for 0.1% of the potential total, which means that there is huge potential for future market growth. With technological progress and cost reduction, it is expected that by 2030, Indonesia's solar installed capacity will jump from the current less than 2GW to more than 10GW, and by 2050 it is expected to exceed 50GW. In particular, large-scale ground power station projects will be accelerated in areas with strong electricity demand such as Sumatra and Java. For example, the planned 100MW solar power station in Sumatra will become an important supplement to regional power supply.
In addition to sunlight resources, Indonesia's abundant land and water resources have also promoted the development of the solar industry. Indonesia has large tracts of undeveloped land, desertified areas and degraded land, which provide ample space for the construction of large-scale ground solar power stations and avoid competition with agricultural land. At the same time, Indonesia has many reservoirs and lakes, such as the waters with 257 floating solar power projects with a potential installed capacity of 14.7GW, where floating solar power stations can be developed, which have multiple benefits such as power, reducing water evaporation, and inhibiting algae growth, and the rich natural resources are effectively utilized.
2. National policy support
The Indonesian government actively promotes the development of solar energy. The "Energy Strategic Plan 2025-2050" clearly defines the development goals of renewable energy, as well as a series of supporting policies such as tax exemptions, subsidies, and simplified approval procedures. For example, the import tax on imported machinery, tools and materials required for solar projects is exempted, and customs clearance is facilitated, which reduces the initial investment cost of enterprises. At the same time, the exemption of 30% of the net profit income tax of solar projects and 10% of the dividend income tax paid by foreign capital have greatly increased the return rate of enterprises investing in solar projects. On October 9, 2024, the Indonesian Ministry of Finance issued the Minister of Finance Regulation No. 69 of 2024 (PMK-69), further optimizing the tax exemption policy and extending the tax exemption period for new investments in certain emerging industries until December 31, 2025, providing more long-term and stable tax incentives for the development of the solar energy industry. The Indonesian Parliament proposed a draft legislation to provide more subsidies for renewable energy projects, including solar power projects, to encourage companies to actively participate in the field of solar power. In order to speed up the implementation of solar energy projects, the Indonesian government has streamlined the project approval process, shortened the approval cycle, and improved the approval efficiency. When applying for solar projects, companies can obtain relevant licenses faster, reducing time costs and speeding up project advancement. The relaxation of the domestic content (TKDN) policy for solar power projects launched in 2024 has lowered the entry threshold for companies and attracted a large influx of domestic and foreign capital. Actively promote the development of rooftop solar energy. According to the plan of the Ministry of Energy and Mineral Resources, 5.7 GW of rooftop solar systems will be deployed between 2024 and 2028, mainly for commercial and industrial users. With the support and improvement of national policies, the return on investment of solar energy projects will be further improved, which will drive more companies to join the solar power industry and expand the scale of the industry.
3. Technological progress and cost reduction
The rapid iteration of solar technology will bring new breakthroughs to Indonesia's solar power. The application of high-efficiency solar cell technology and intelligent systems will greatly improve the efficiency and stability of solar power. For example, the application of the new generation of PERC cell technology can increase the conversion efficiency of solar cells to more than 23%, reducing the unit power cost. At the same time, the intelligent monitoring system can timely detect and solve power system failures and reduce maintenance costs through real-time monitoring and data analysis. With the continuous maturity and popularization of technology, it is expected that the cost per kilowatt-hour of solar power in Indonesia will drop by 30%-50% in the next 5-10 years, which will have strong market competitiveness compared with traditional energy.
4. Surge in market demand
With the rapid development of Indonesia's economy and the continuous growth of its population, the demand for electricity has shown a continuous upward trend. The demand for electricity in households, industry and commerce is growing. Some remote areas and islands that have not yet been connected to the national grid urgently need to install simple and low-cost solar power systems to obtain stable power support. By building solar power stations, they can meet the power needs of local residents. At the same time, they can promote the development of tourism and fisheries. Solar energy has great development opportunities.
5. Distributed solar usher in a golden period of development
Given the current situation of scattered islands and insufficient grid coverage in Indonesia, distributed solar will become the key to solving the problem of power supply in remote areas. Industrial and commercial rooftop solar and household solar systems will develop rapidly driven by policy support and market demand. In industrial parks in large cities such as Jakarta and Surabaya, industrial and commercial rooftop solar projects will become an important choice for enterprises to reduce electricity costs and achieve green transformation; in rural areas and remote islands, household solar systems will provide residents with a stable power supply and improve their quality of life. It is estimated that by 2030, the installed capacity of distributed solar will account for 30%-40% of Indonesia's total solar installed capacity. Solar power solar is developing rapidly, which is very suitable for the application of off-grid solar inverters.
6. International cooperation accelerates industrial upgrading
Indonesia actively cooperates with international organizations and other countries to inject new impetus into the development of the solar energy industry. During the 2022 G20 Summit, Indonesia issued the "Joint Energy Transition Partnership (JETP)" and obtained a $20 billion commitment for energy transformation. Cooperate with China, Japan, South Korea and other countries in solar technology research and development, project construction, talent training and other aspects, and introduce advanced technology and management experience. For example, cooperate with Chinese companies to learn from their mature technologies in solar module manufacturing and power station construction to improve the technical level of local industries; cooperate with international financial institutions to obtain low-interest loans and financing support to ease the financial pressure of solar project construction.
7. Superior geographical location
Located in the center of Southeast Asia, Indonesia is an important hub connecting the Pacific and Indian Oceans and occupies an important position in international trade and regional economic cooperation. It is conducive to the import and export trade of products related to the solar energy industry. On the one hand, it can export solar power or related equipment to neighboring countries with strong electricity demand, such as Singapore and Malaysia; on the other hand, it is also conducive to attracting investment from neighboring countries and jointly developing solar projects. At the same time, as the ASEAN economic integration process advances, Indonesia's solar energy industry can leverage the regional economic cooperation platform to expand the market scale, reduce production costs, enhance the overall competitiveness of the industry, and drive the coordinated development of the regional economy.
V. Types of solar inverters suitable for Indonesia
In Indonesia, a country with many islands, the grid coverage is low and the power supply is unstable. Solar power systems have attracted much attention in recent years. Various types of solar inverters have appeared on the market. Choosing the right solar inverter is the key to the entire solar system. Generally, inverters are divided into: off-grid solar inverters, on grid solar inverters, and hybrid solar inverters. Below we will take a closer look at the types of solar inverters suitable for Indonesia:
1. Off-grid solar inverters
Off-grid solar inverters operate independently of the grid, converting the direct current (DC) generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC), which is directly supplied to the load, and the excess power can be stored in batteries. In Indonesia, due to the large number of islands and the scattered geographical structure, remote islands in the east such as Maluku and Papua have insufficient grid coverage, and about 27 million people cannot stably access the main grid. Diesel generators have become the main power supply method, but they are costly and polluting. Off-grid solar inverters are used in these remote areas far from the power grid. They can be used with solar panels and energy storage systems to ensure 24-hour uninterrupted power supply, provide stable electricity for local residents, meet basic electricity needs such as lighting and home appliance use, reduce power costs, and reduce environmental pollution; they can also provide power guarantee for small commercial places and communication base stations in remote areas, and help regional economic development. For remote areas in Indonesia, although the initial investment is large, in the long run, it can solve the electricity problems of local residents and enterprises and has high economic and social benefits.
For example, in the villages of the Maluku Islands, off-grid inverters are used with small solar systems and batteries to solve the long-term power shortage problem and reduce the electricity costs of residents. Xindun's off-grid solar inverter has a wide voltage input range and MPPT (maximum power point tracking) function, which can maximize the solar energy conversion efficiency when the light conditions change, and ensure stable operation in complex environments.
2. On grid solar inverters
On grid solar inverters convert the direct current (DC) generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) with the same frequency and phase as the power grid, and directly connect to the public power grid. They are suitable for areas in Indonesia where the power grid is stable and "net metering" is allowed. The distribution of Indonesia's power grid is uneven. The Java-Bali region has sufficient power supply, but other regions generally face power shortages. However, with the development of industry and commerce, the demand for electricity continues to grow. In the industrial and commercial rooftop solar projects in the region, on grid inverters play a key role. For example, in industrial parks in large cities such as Jakarta and Surabaya, enterprises install rooftop solar systems and sell excess electricity to the grid through on grid inverters, which can not only reduce their own electricity costs, but also obtain additional income.
3. Hybrid solar inverters
Hybrid solar inverters combine the functions of off grid and on grid inverters. When there is grid, it can realize on grid power and connect excess power to the grid. When the grid is out of power or unstable, it automatically switches to off-grid mode, uses solar energy and battery storage to power the load, and intelligently manages solar power, battery charging and discharging, and grid interaction. Hybrid solar inverters are suitable for areas with unstable power supply in Indonesia, such as Sumatra and Kalimantan, where only some areas are connected to the grid, but the grid is unstable and often faces problems such as power outages and low voltage.
Hybrid solar inverters can be used in residential, hospital, school and other places. When there is sufficient sunlight during the day, the system is connected to the grid for power; at night or on cloudy days, if the grid is normal, it draws power from the grid. When the grid fails, it relies on the power stored in the battery to ensure the normal operation of the load. Although the initial investment cost is high, for some companies that want a more stable power supply, they can not only obtain a reliable power supply, but also obtain a long-term return on investment.
VI. Recommendation of solar inverters in Indonesia
With the rise of Indonesia's solar market, China's solar inverter product exports have continued to expand, occupying an important market share. As the core equipment of the solar power system, the performance of the inverter directly affects the power efficiency and stability of the entire solar system. So how to choose solar inverter that meets Indonesia's power needs? Below we will recommend five of Xindun's most popular solar inverters in the Indonesia market:
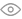
Xindun HFP Series Hybrid Solar Inverter
Xindun HFP series hybrid solar inverter provide DC 12V/24V/48V to AC 220V/230V/240V, 1.3KW-12.3KW
The Xindun HFP series is a high-frequency bidirectional energy storage design on-grid and off-grid hybrid solar inverter that integrates on-grid and off-grid functions to meet the needs of various power environments in Indonesia. In view of the unstable power grid in Indonesia and the difficulty of power supply in remote areas, users can flexibly set the off-grid mode, on-grid mode or hybrid operation mode according to actual needs. It is suitable for different power environments in Indonesia, whether it is remote islands, rural areas with frequent power outages, or industrial and commercial users with unstable power supply but connected to the grid, they can all operate stably. The inverter supports solar priority, and gives priority to solar power supply when there is sufficient sunlight during the day. The excess power can be stored in the battery or fed back to the grid to achieve the surplus power access to the grid. When there is insufficient light or the load still needs to be powered at night, the system automatically switches to battery or mains power supply to ensure that users' power supply is not interrupted. Built-in MPPT solar controller, with ultra-wide solar input voltage of 500Vdc, maximum efficiency of solar power, efficiency up to 99%.
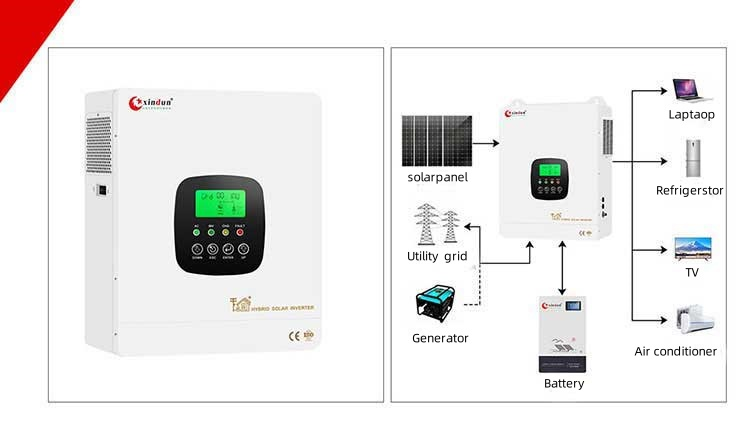
Xindun HFP-C Series Hybrid Solar Inverter
Xindun HFP-C series hybrid solar inverter provide DC 24V/48V to AC 220V/230V/240V, 4.3KW-12.3KW
XIndun HFP-C series is a newly upgraded dual AC output on-grid and off-grid hybrid solar inverter based on HFP. Its output phase, voltage and frequency are the same, which can meet a variety of power needs. And it has been significantly upgraded in appearance design, showing a simple and stylish style. The use of LED intelligent RGB ring light strip not only adds personalized lighting effects, but also displays the working status of the inverter. Users can clearly understand the operation of the inverter at a glance, which greatly improves the convenience of use. The brightness of the RGB ring light strip can be freely adjusted, and eight colors are available, allowing users to enjoy the convenience brought by technology while also better controlling the use of energy. It is very suitable for solar projects in Indonesian homes, shops or remote areas.
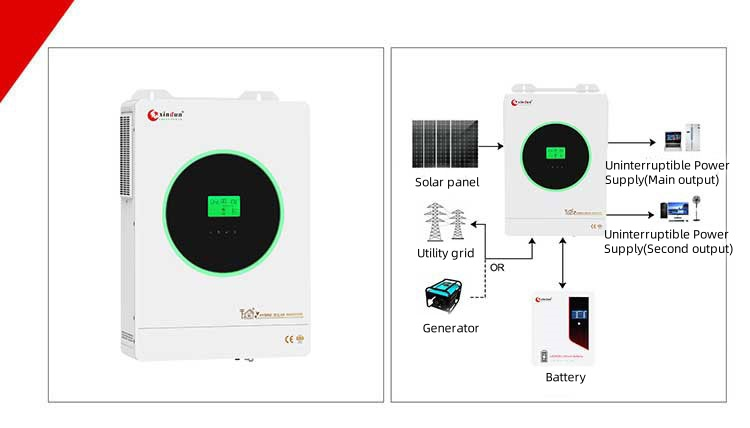
Xindun HDSX Series Three Phase Solar Inverter
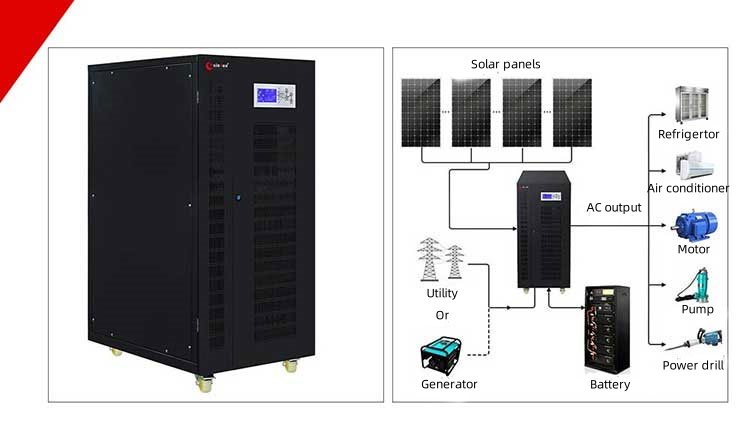
Xindun HDSX series three phase solar inverter provide DC 48V/96V/192V/384V to AC 380V/400V, 3.2KW-160KW
Xindun HDSX series is a three-phase solar inverter suitable for industrial and commercial use, used for high-power loads such as factories, large commercial buildings, warehouses and agricultural electricity. It supports 100% unbalanced load, has three-input and three-output functions, adapts to various battery types, meets diverse power needs, and provides stable and reliable power guarantee for corporate users. It is suitable for areas with asymmetric or fluctuating power supply in urban and rural areas or industrial parks in Indonesia, improving system stability and compatibility. At the same time, it can also be used as a UPS. When the mains power is normal, it stabilizes the mains power and supplies it to the load, and charges the battery at the same time. When the mains power is interrupted, it can stabilize the grid voltage and supply power, and charge the battery at the same time; when the mains power is interrupted, the system instantly switches to battery power supply to seamlessly ensure the continuous operation of critical loads. Help enterprise users effectively avoid economic losses caused by equipment damage and production interruption.
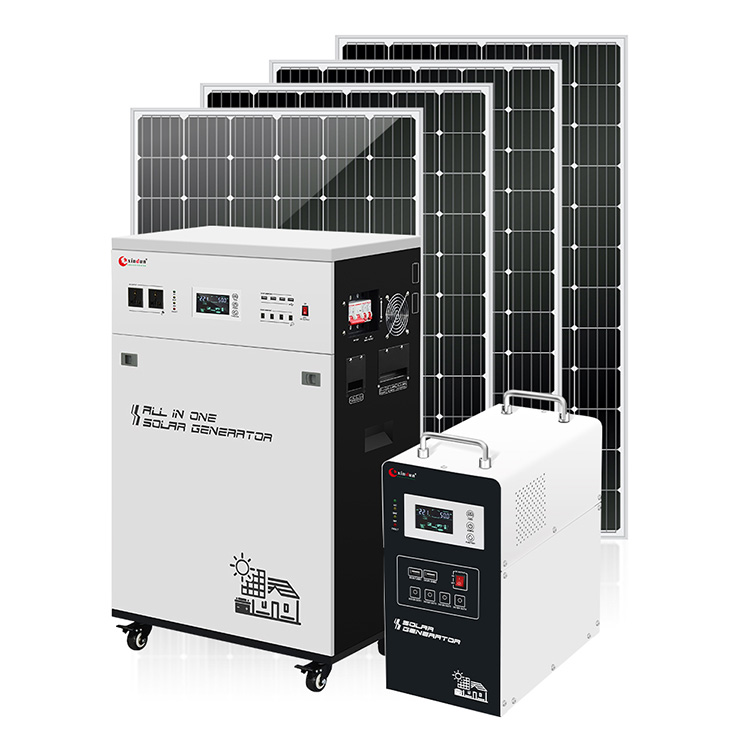
Xindun ESS-Li Series All In One Solar Generator

Xindun ESS-Li Series All In One Solar Generator provide DC 12V/24V/48V to AC 110V/120V/220V/230V/240V, 300W-7000W
Xindun ESS-Li series is solar generator with integrated inverter, MPPT solar inverter and lithium battery. It is easy to install and suitable for use in remote islands, villages and areas lacking electrical resources. Equipped with USB, DC ports and AC plug-in sockets, it meets the diverse power needs of homes and small commercial places. It supports three charging methods: solar energy, mains power and diesel engine. Even in the case of insufficient sunlight or frequent interruptions of mains power during the rainy season in Indonesia, it can flexibly guarantee power supply and improve the continuity and stability of energy acquisition. It supports Wi-Fi or APP remote monitoring, so users can grasp the operating status of the equipment at any time, intelligently manage power use, and improve energy efficiency. Help users achieve autonomous, economical and efficient energy management. At the same time, ESS-Li is equipped with a complete power protection mechanism and battery BMS monitoring function, which can effectively cope with the voltage fluctuations and high temperature and high humidity environment common in Indonesia, extend the service life of the equipment, and ensure the safe and reliable operation of the system.
Xindun LF Series Solar Power Inverter

Xindun LF solar power inverter provide DC 12V/24V/48V to AC 110V/120V/220V/230V/240V, 1KW-12KW
Xindun LF series is a lowfrequency solar inverter that outputs pure sine waves. It is suitable for the complex power environment in Indonesia. It has a startup peak power of up to 3 times, and can easily drive high-power equipment such as air conditioners and water pumps. It is suitable for use in remote island areas in Indonesia. It has a newly added fault code query, which is convenient for users to troubleshoot problems in time and can be easily maintained even in areas with inconvenient services. Compatible with diesel and gasoline generator inputs, it can obtain a stable power supply even in harsh environments. The dual-use design for industrial and civil use supports wall-mounted installation. It is suitable for homes, small commercial places, communication base stations, etc., helping Indonesian users obtain safe, stable and economical clean electricity.
VII. Why is Xindun a trustworthy inverter supplier?
Since our establishment in 2006, Xindun has been focusing on the research and development, production and global sales of solar inverters, controllers, energy storage batteries and complete solar systems. We have a professional R&D team of more than 30 people to ensure that our products always maintain industry-leading performance and stability. All Xindun Power products have also obtained a number of international professional certifications such as CE, IEC, CCC, etc., and are widely used in household electricity, commercial operations, agricultural production and industry. In view of the numerous islands in Indonesia, uneven grid coverage, and unstable power supply in some areas, our solar inverters can effectively improve the utilization rate of solar power and meet the strong demand of the Indonesian market for "high cost performance + high reliability".
We have a modern production base of more than 10,000 square meters, 12 intelligent production lines, and a monthly production capacity of more than 50,000 machines. We have been deeply involved in the Southeast Asia market for many years and learned that Indonesia has a large island structure and extensive rural and remote areas. Many areas have long faced problems with unstable power grids or even no electricity. Our off-grid solar inverters are very popular in the region. We have also established long-term business relations with the Middle East, Latin America and other regions, and established branches in Indonesia and the Philippines with warehouse centers and marketing centers to provide timely technical support and services to the Southeast Asia market. We can respond quickly to customer orders, ensure delivery efficiency, and provide strong supply chain support for Indonesian partners.
As a professional manufacturer in China's solar industry, Xindun Power has a deep understanding of the energy status and development needs of the Indonesia market. Against the background of the continuous deepening of the "Belt and Road" cooperation between China and Indonesia, Xindun relies on China's perfect solar manufacturing industry chain and combines its own technical advantages in the field of solar inverters and energy storage systems to provide Indonesian customers with cost-effective and stable product solutions. We have successfully exported a number of off-grid and hybrid inverters to Indonesia, which are widely used in various scenarios such as home residences, commercial buildings and remote areas, and have won good market feedback.
If you are interested in Xindun's solar inverters or system solutions, please visit our official website and leave your information and needs in the customer service window at the bottom of the page (https://www.xinduninverter.com/). Our team will contact you as soon as possible during working hours to provide you with professional and efficient services and support.


 Solar Inverter
Solar Inverter





 Hybrid Inverter
Hybrid Inverter





 Power Inverter
Power Inverter





 Split Phase Inverter
Split Phase Inverter

 Energy Storage Inverter
Energy Storage Inverter




 3 Phase Inverter
3 Phase Inverter




 Solar System Kits
Solar System Kits





 Solar Charge Controller
Solar Charge Controller


 Solar Battery
Solar Battery



 Asia
Asia
 Africa
Africa



 South America
South America
 Europe
Europe

 North America
North America

 Oceania & Antarctica
Oceania & Antarctica









 Home
Home Recommendations For Solar Inverters In India
Recommendations For Solar Inverters In India  Top Selling Products
Top Selling Products














