How to Set the Charging Current of Hybrid Inverter?
 Jul 26,2025
Jul 26,2025
 XINDUN
XINDUN
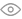
A hybrid inverter is a hybrid and complementary solar inverter that can be powered by PV + mains + battery. It has the characteristics of both off grid and on grid inverters, and can be set to off grid mode, on grid mode, and hybrid mode. Among them, the off grid mode and hybrid mode are the modes frequently used by many users, and the charging current setting in the inverter is also a very important operation. Reasonable setting of the charging current can ensure the safe and efficient charging of the battery and extend the battery life. So how to set the charging current of the hybrid inverter? Below, Xindun will give you a detailed introduction to the charging current setting and usage scenarios of the Xindun hybrid inverter.
The difference in charging current
The HFP series hybrid inverter of Xindun has three charging current parameters, namely, the maximum mains charging current, the maximum PV charging current, and the maximum charging current (mains + PV).
The maximum PV charging current refers to the maximum charging current allowed by the inverter when the battery is charged only by the power generated by the solar panel.
The maximum mains charging current refers to the maximum charging current allowed by the inverter when the battery is charged by the mains alone. This parameter plays a key role when the solar power is insufficient and the battery needs to be charged by the mains. For example, on cloudy days or at night, the PV panel cannot generate electricity normally. By setting the maximum mains charging current reasonably, the battery can be quickly fully charged.
The maximum charging current (PV + mains) refers to the maximum limit value of the sum of the charging currents of PV and mains when the battery is charged at the same time. It comprehensively considers the upper limit of the total current when the two charging methods of mains and PV are acting at the same time. Due to the technology of different inverter manufacturers, the setting logic of technical parameters will be different. When setting the maximum charging current value, Xindun’s solar inverter also sets the maximum PV charging current value, and at the same time limits the maximum PV charging current value. For example, if the maximum charging current is set to 100A, the maximum PV charging current value is also 100A, but after the mains charging current is set to 30A, the maximum PV charging current value is 70A (maximum charging current value 100A - maximum mains charging current value 30A). Therefore, in actual operation, users need to carefully read the product manual of Xindun inverter and understand its parameter setting instructions.
Inverter charging mode
In previous articles, Xindun introduced in detail the charging modes of Xindun hybrid inverters. How to use charging priority? - There are three charging modes in the Xindun hybrid inverter series:
"SNU" charging mode - PV and mains are charged at the same time, and PV is consumed first
"OSO" charging mode - only PV is charged, and mains does not participate in charging
"CSO" charging mode - PV is charged first, and mains only intervenes when there is no PV
Charging mode selection and charging current setting
The following is a detailed introduction of the charging mode and charging current settings according to different scenarios of users (for reference only, need to be set according to actual conditions). Taking the Xindun HFP hybrid inverter 6300W as an example, its maximum mains charging current is 80A, the maximum charging current is 120A (maximum PV charging current is 120A), and the default values are 30A and 60A respectively.
1. Only mains available scenario
Scenario: For example, during the night period or in rainy weather for many consecutive days, there is insufficient PV energy or no PV energy supplement, and the battery can only be charged by mains.
Charging mode selection: In this case, there is only one charging source, namely the mains, so in addition to the "OSO" charging mode, you can choose the "SNU" and "CSO" charging modes.
Charging current setting: Set the "maximum mains charging current" value according to the battery type and capacity.
Lead acid battery: It is generally recommended to set the charging current according to 0.1C - 0.2C (C is the battery capacity). Taking the Xindun HFP hybrid inverter 6300W as an example, it is equipped with a 48V 200Ah lead-acid battery, so the "maximum mains charging current" can be set at around 20-40A. The maximum mains charging current setting range of the Xindun HFP hybrid inverter 6300W is 5A-80A, and it cannot exceed this range when setting.
Lithium battery: refer to the charging current range recommended by its lithium battery manual, which is usually 0.5C. For example, taking a 51.2V 100Ah lithium battery as an example, the product manual of the lithium battery recommends a standard charging current of 50A, then the "maximum mains charging current" value of 50A can be set. If the standard charging current of the lithium battery exceeds the upper limit of the inverter's mains charging current, the upper limit of the inverter shall prevail and cannot exceed its range (5A-80A).
2. Only PV available scenarios
Scenario: If the user is in a remote area, there is no mains access or the mains power is often unstable, but the local light resources are very sufficient, and the battery is completely charged by solar panels.
Charging mode selection: In this scenario, the user can choose the "OSO" charging mode (only PV charging, the mains power does not participate in charging) to ensure that the inverter will only use photovoltaic energy for charging.
Charging current setting: The "maximum PV charging current" of the Xindun HFP hybrid inverter 6300W model is 120A, which can be adjusted according to the power of the solar panel assembly and the battery charging demand.
The power of the PV panel assembly is small: If the power of the PV panel assembly installed by the user is small, the maximum PV charging current setting can be appropriately reduced to avoid frequent adjustment of the working state of the inverter due to unsatisfactory current demand. For example, if the PV panel assembly can only stably output a charging current of 5A, the "maximum PV charging current" can be set to 10A.
The PV panel has a large power and the battery can withstand it: If the PV panel component has a large power and the battery can also withstand a large charging current, then the "maximum charging current" can be set to a value close to the value allowed by the inverter, which can be set to 100A-120A.
3. Scenarios where both mains and PV are available
① Give priority to PV charging scenarios
Scenario: The purpose is to maximize the use of clean energy and reduce the consumption of mains electricity. For example, during periods of sufficient sunlight and high local mains electricity rates.
Charging mode selection: Select the "SNU" charging mode (PV and mains charging at the same time, PV priority), which will give priority to consuming PV, and the mains will only supplement when PV is insufficient.
Charging current setting: First, determine a suitable total charging current based on the battery type and capacity. Then set the maximum charging current close to this value, but not exceeding the inverter's charging current limit range of 5-120A. The maximum mains charging current can be set to a relatively small value to ensure that PV can be charged first. For example, if the battery charging current standard is 100A, then the "maximum mains charging current" can be set to the default value of 30A, and the "maximum charging current" can be set to 120A (maximum PV charging current 90A), so that PV power can give priority to meeting the charging needs, and the insufficient part can be supplemented by the mains.
② Fast charging scenario
Scenario: When the battery power needs to be replenished urgently, and both the mains and PV resources are relatively sufficient.
Charging mode selection: Also select the "SNU" charging mode, and give full priority to using PV and mains to supplement the battery.
Charging current setting: Set the maximum charging current value to the larger value that the battery can withstand, and at the same time, adjust the mains charging current reasonably in combination with the actual power generation of the PV panel. Assuming that the photovoltaic panel component can currently provide a charging current of 60A, and the battery can withstand a total charging current of 10A, then the "maximum mains charging current" can be set to 60A and the "maximum charging current" can be set to 120A (maximum PV charging current 60A).
4. PV is preferred and the use of mains power is minimized
Scenario: Users want to rely on PV for charging as much as possible, and only enable mains power supplementation when PV is seriously insufficient. For example, users are pursuing the use of green energy, and the mains power supply in the area is not stable.
Charging mode selection: Select the "CSO" charging mode (PV is prioritized for charging, and the mains power is only involved when there is no PV).
Charging current setting: The maximum charging current can be set slightly higher than the maximum charging current that the PV module can provide under normal circumstances to cope with the sudden increase in light. The "maximum mains power charging current" can be set to a smaller value (5A-30A) or the default value (30A), because it mainly relies on PV for charging, and the mains power is only used in special circumstances. For example, the PV panel assembly can normally provide a charging current of 50A, and the "maximum mains power charging current" can be set to 5A-30A, and the "maximum charging current" can be set to 70-120A (maximum PV charging current 65A-90A).
In different usage scenarios, users need to flexibly adjust the charging current parameters of the inverter according to the actual situation, and also adjust them in combination with factors such as solar panel power, inverter parameters, battery type and capacity to ensure charging effect and equipment safety. In areas with abundant PV resources, the maximum PV charging current can be appropriately increased to make full use of solar energy; in areas with unstable mains supply, the maximum mains charging current and the maximum charging current (PV+ mains) should be set carefully to avoid damage to the inverter and battery due to current fluctuations.
Xindun HFP Hybrid Inverter
Xindun 1KW-12.3KW HFP series is a hybrid inverter with on grid and off grid modes. The three modes can be switched flexibly, it also supporting batteryfree operation mode, PV/mains/battery synergistic hybrid complementation, up to 500V PV input voltage, 80V-450V PV DC voltage mppt tracking range. High frequency pure sine wave output, inverter conversion efficiency up to 94%. Details are as follows:
|
Model : HFP |
10212 |
13212 |
18212 |
18224 |
23224 |
33224 |
43224 |
50248 |
63248 |
83248 |
103248 |
123248 |
|
|
PV |
Max PV Input Power |
1500W |
2000W |
2500W |
2500W |
3000W |
5000W |
6000W |
7000W |
4500W*2 |
6000W*2 |
6000W*2 |
|
|
MPPT Tracking Voltage Range |
30VDC-240VDC |
40VDC-350VDC |
40VDC-450VDC |
80VDC-450VDC |
|||||||||
|
Rated Voltage |
180VDC |
240VDC |
280VDC |
||||||||||
|
Max PV Input Voltage voc |
300VDC |
400VDC |
500VDC |
||||||||||
|
Max PV Input Current |
13A |
15A |
18A |
27A |
18A*2 |
22A*2 |
27A*2 |
||||||
|
MPPT Tracking Channels |
1 Routed |
2 Routed |
|||||||||||
|
Battery& |
Max PV Charging Current |
||||||||||||
|
60A |
80A |
100A |
60A |
80A |
120A |
150A |
100A |
120A |
150A |
180A |
200A |
||
|
Max AC Charging Current |
40A |
50A |
65A |
35A |
50A |
80A |
100A |
60A |
80A |
100A |
120A |
140A |
|
|
Max Charging Current |
60A |
80A |
100A |
60A |
80A |
120A |
150A |
100A |
120A |
150A |
180A |
200A |
|
If you want to know more about Xindun hybrid inverter, please feel free to contact us. Xindun team will provide one to one professional service.

 Solar Inverter
Solar Inverter





 Hybrid Inverter
Hybrid Inverter





 Power Inverter
Power Inverter





 Split Phase Inverter
Split Phase Inverter

 Energy Storage Inverter
Energy Storage Inverter




 3 Phase Inverter
3 Phase Inverter




 Solar System Kits
Solar System Kits





 Solar Charge Controller
Solar Charge Controller


 Solar Battery
Solar Battery



 Asia
Asia
 Africa
Africa



 South America
South America
 Europe
Europe

 North America
North America

 Oceania & Antarctica
Oceania & Antarctica









 Home
Home How Is the Solar Inverter Market Developing In Bangladesh?
How Is the Solar Inverter Market Developing In Bangladesh?  Top Selling Products
Top Selling Products














